*Mesothelioma Epithelial :-
Mesothelioma Epithelial acells have a definite structure with visible nuclei. This is the most common variant of this type of cancer, accounting for about 60 percent of all cases. This type of mesothelioma develops when malignant cells develop on any of the mesothelial linings. When examined under a microscope, these cells are of a uniform size and shape, and resemble normal, healthy epithelial cells.
Mesothelioma Epithelial cells also bear a strong resemblance to adenocarcinoma cells, which are also associated with lung tissue. Patients who have been diagnosed with adenocarcinoma should also be examined for mesothelioma as well.
Variants
Papillary mesothelioma is an example of epithelial mesothelioma ;other variants include any of the following :
- Signet Ring - Single File - Adenoid Cystic - Tubulopapillary - Histiocytoid - Micro cystic - Macro cytic - Glomeruloid - Diffuse -NOS - Small Gell - Deciduoid - Pleomorphic - In Situ *Muoin Positive - Well-Different ed Papillary *Gaucher Cell-Like
What differentiates these various types are the shape , size and formation of the cells. This can Determine what course of treatment is appropriate for the patient's situations.
Mesothelioma Epithelial and asbestos
Once asbestos fibers are inhaled, they become lodged in the lung tissue , where they remain indefinitely . Mesothelioma2all is associared with hard, crystalline amphibole over time,causing chronic inflammation that ultimately results in malignancy, The disease has a very long latency period, which can be anywhere from five to seventy-five years. The symptoms of the disease are
also similar to other respiratory illnesses, which is why mesothelioma has historically been so difficult to diagnose.
*Mesothelioma Sarcomatoid :-
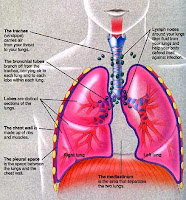
Mesothelioma is a cancer that at tacks the lubricative layer lining the mside of the chest and abdomen and the internal organs. Pathologists categorize cases according to levels of criteria, which are as follows:
Locations :
- Lungs (pleural)
- Abdomen (peritoneal)
- Heart(pericardial)
- Abdomen (peritoneal)
- Heart(pericardial)
Stage:
*Stage I - Mesothelioma cells have started to form
*Stage II - Mesothelioma has spread locally
*Stare III-Mesothelioma has spread to adjoining areas
*stage IV -Mesothioma has begun to metastasize
*Stage II - Mesothelioma has spread locally
*Stare III-Mesothelioma has spread to adjoining areas
*stage IV -Mesothioma has begun to metastasize
Cellular Structure:
*Epithelial (organized and structured)
*Sarcomatoid (random and irregular)
*Biphasic (a mix of epithelial and Sarcomatioid)
*Desmoplastic ( a variation of the Sarcomatiod Variety )
*Sarcomatoid (random and irregular)
*Biphasic (a mix of epithelial and Sarcomatioid)
*Desmoplastic ( a variation of the Sarcomatiod Variety )
Cellular structure is determined by an actual visual exam mation of the cells under a microscope.
About Mesothelioma Sarcomatoid
Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma accounts for approxmately 10 - 15 perecent of all diagnoses.
The mesothelioma cells in this case are elongated and spindle - shaped, and are arranged in a
rather haphazard way .Sarcomatoid cells also lack a nucleus, unlike Epithelioid cells,which have clearly visible nuclei.
The desmoplastic variety of mesothelioma sarcomatoid is difficult to distinguish from healthy tissue in many cases, making an accurate diagnosis challenging .
Diagnosis
Once symptomes have been cataloged and a history of asbestos exposure determined, the next step is to look inside the body- initially with x-rays, followed up by more sophisticated imaging such as CT scans or MRI s. If these images reveal serious abnormalities ,a bipsy (tissue samples ) will be ordered. These are examined and analyzed at a lab, which usually confirms or contradicts the diagnosis.
When it comes to the mesothelioma sarcomatoid , traditional methods of biopsy pose additional challenges; the normal "needle core" method often results in false information, as Sarcomatoid cells are often similar in apperance to benign fibrous tissue.
Additionally, histological methods of diagnosis often make it difficult to distinguish between Mesothelioma Sarcomatoid and other types of unrelated Mesothelioma2all sarcomatoid cancer .
A precise and accurate diagnosis is vital, because a misdiagnosis can lead to an inappropriate course of treatment being prescribed; it is a good idea to get a second and even a third opinion if mesothelioma is suspected.
Mesothelioma Biphasic :-
Mesothelioma Biphasic is the second most common cellular form of this disease, accounting for 20-40 percent of all known cases. As the name implles, mesothelioma biphasic is a mixture of two types of cancer cells .
Characteristics
Unlike the more common Epithelioid type, biphas mesothelioma cells lack a specific structure. This type of mesothelioma is a mix of Epithelioid and sarcomatoid cells.
Whereas the former has a clearly visible nucleus and is found in uniform, organized arrangements and tend to be of a single shape, Sarcomatoid cells are more oval or oblong shaped and have no easily identifiable nucleus. Aithough both types are present in a biphasic tumor, they have a tendency to form in differetiated groups;they are not usually found in the same area of the tumor.